What is a Whole-House Filtration System?
A whole-house filtration system is a comprehensive solution for filtering the water that flows through your entire home. It’s installed at the main water supply line to ensure that every tap and appliance receives filtered water, providing consistent quality throughout.
These systems are essential to many homeowners because they offer a dependable way to maintain clean water across your entire household. By removing sediment, chemicals, and other contaminants, a whole-house filtration system ensures that water is cleaner for bathing, drinking, cooking, and laundry.
With whole-house filtration systems in place, households can enjoy peace of mind knowing their water is cleaner, healthier, and available from every outlet in their home.
Benefits of Whole-House Filtration Systems
Health
Contaminant Removal
Whole house filtration systems are designed to filter out harmful contaminants such as chlorine, heavy metals, pesticides, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can affect health. By addressing these issues, the system provides safer water for drinking, cooking, and hygiene.
Allergen Reduction
By filtering out sediment and chlorine, these systems help reduce allergens that could irritate the skin or exacerbate respiratory conditions, especially important for people with sensitivities or allergies.
Convenience
Centralised Solution
A whole house system eliminates the need for separate filters at each outlet, saving time and effort on maintenance and replacement.
Appliance Longevity
Some specific filters can remove sediments and minerals before they enter your appliances to help reduce scale buildup. thus extending the lifespan of your dishwasher, water heater, washing machine, and other devices. The ARAGON filter has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing scale (calcium and magnesium deposits from water for example.
Consistent Quality
Whether you’re drinking from the kitchen tap, taking a shower, or running a load of laundry, you receive the same quality water, ensuring a consistent and pleasant experience.
Environmental Impact
Reduced Plastic Waste and Carbon Footprint
By reducing the reliance on bottled water and single-use filters, these systems can significantly cut down on plastic waste and contribute to a cleaner environment.
On top of that, the reduced production and transportation of bottled water can lead to a smaller carbon footprint, helping to lower overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Types of Whole-House Filtration Systems
Four main types of filtration systems can be used in whole-house filtration. Each of these offers unique strengths and often works best in combination with others to ensure comprehensive water treatment throughout your entire home.
Sediment Filters
Sediment filters primarily target particles like dirt, sand, rust, and other larger debris suspended in the water supply.
These systems are ideal for homes with high sediment levels due to old plumbing, local water conditions, or well water. They often serve as the first stage in a multi-stage filtration system, doing the hard work of removing sediment and protecting other filters downstream.
Carbon Filters
Carbon filters come in many different forms and the quality of the final filtered product can vary depending on the actual source of the carbon. Typically, carbon filters are designed to reduce chlorine, unpleasant tastes, and odours. They can also target certain organic compounds, pesticides, and some heavy metals.
They’re great for households wanting to improve the taste and odour of their water. They are often paired with other filters to remove a broader range of contaminants.
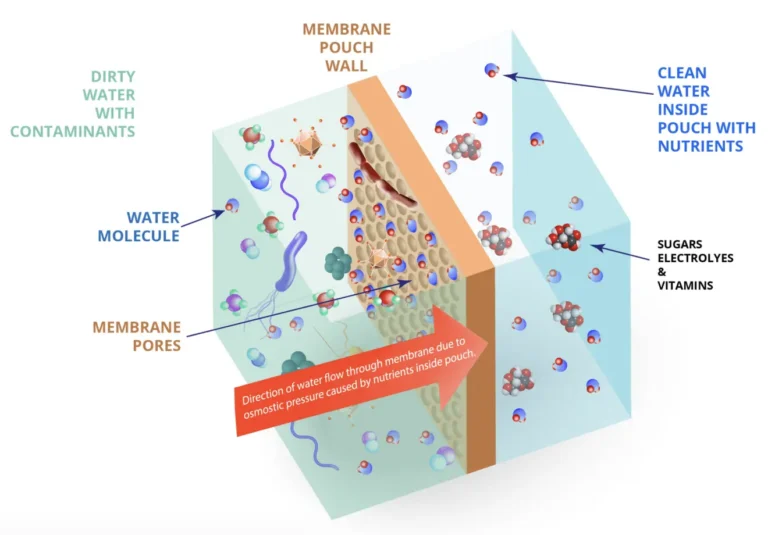
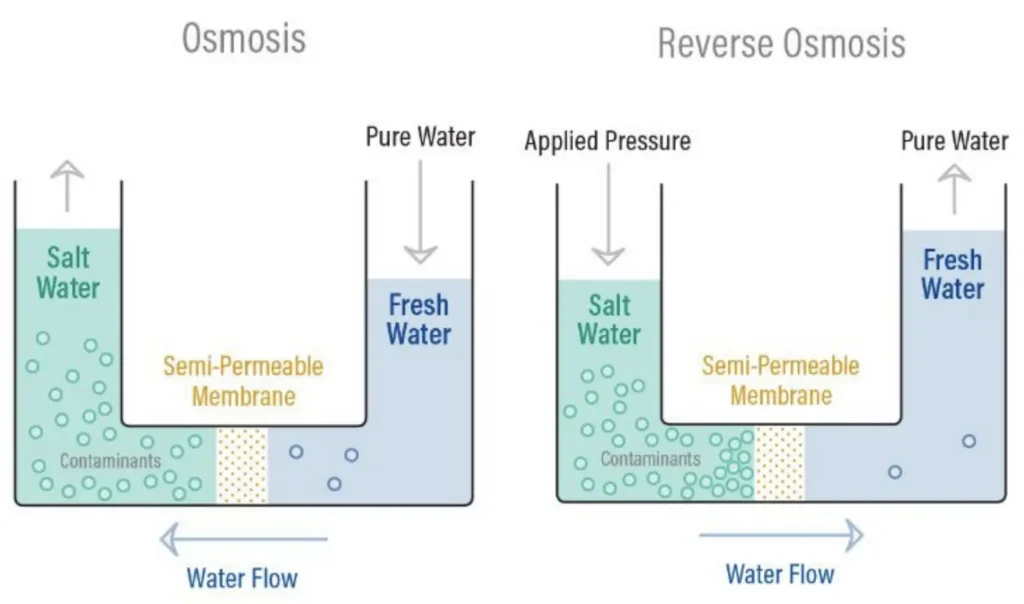
Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse osmosis (RO) systems work by pushing water through a semipermeable membrane, which filters out a vast array of impurities, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, and microorganisms.
These systems can be suitable for homes where the local water supply may have high contamination levels or concerns about specific contaminants like nitrates and lead. However, RO systems can reduce water pressure and require a pre-filtration system. Additionally, RO systems can cause excess water usage due to the wastage of water caused by the filtration
Ultraviolet (UV) Purifiers
UV purifiers are technically not water filters but can be used as part of filtration systems. UV purifiers use ultraviolet light to kill or deactivate bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens in the water. They are often used alongside sediment and carbon filters for a comprehensive solution.
These systems can be foreseen in well water or in regions where microbial contamination is a risk. They ensure safe drinking water by effectively neutralising biological contaminants.
How to Choose a House Filtration System
Choosing the best whole-house filtration system for your home can be achieved by evaluating your unique water quality needs and considering technical factors like capacity and flow rate.
Assessing Your Water Quality Needs
The first step is to understand the quality of your water. If you’re using a well or another private source, your filtration needs will differ significantly from those connected to municipal supply.
You can use a water test to pinpoint the specific contaminants present, such as chlorine, heavy metals, pesticides, or bacteria. When considering your water quality needs or testing, you should also factor in any health concerns, like allergies or sensitivities, that might require more advanced filtration. This assessment will help you identify which type of filtration system will be the most effective.
Considering System Capacity and Flow Rate
Next, think about the demands of your household. The system needs to handle your daily water consumption and deliver an adequate flow rate across all taps and appliances. A household with several people requires a filtration system that can handle high water usage without causing a significant drop in pressure.
Importance of Compatibility with Local Water Regulations:
Finally, make sure your filtration system is compatible with local water regulations. Some systems, particularly reverse osmosis, can produce wastewater that needs proper disposal, so it’s essential to comply with local rules about discharges.
Installation codes must also be adhered to, which may require professional assistance for proper setup. Verifying these factors beforehand ensures that your system will operate smoothly and stay within regulatory guidelines.
Finding a Whole-House Filtration System
Investing in a whole-house filtration system may be a smart choice for any household prioritising health, convenience, and sustainability.
These systems offer comprehensive filtration by removing a wide range of contaminants like chlorine, sediments, heavy metals, and bacteria, ensuring that the water throughout your home is clean and safe. With the right system capacity and flow rate, everyone in your household will enjoy reliable, high-quality water from every tap and appliance. Plus, reducing the need for bottled water and single-use filters can lessen your environmental footprint.
If you’re ready to learn more about these systems, Aussie Water Coolers offers a range of whole-house filtration systems tailored to meet varying household needs. Whether you’re looking for sediment filters, reverse osmosis, or you’re not sure yet, our solutions can help deliver cleaner water that complies with local water regulations. Visit our online shop today to explore our filtration options and speak to our team about choosing the perfect system for your home.
We offer free no obligation, non-hard sell advice at all times, so please feel free to contact us to learn more.
In Australia it’s hot and often uncomfortable. If you follow our Facebook page, you will you know we remind everyone constantly to make sure that they are drinking enough, and let’s face it, sometimes it’s hard!
We become water logged and drinking another glass of plain old straight water from the cooler becomes effort. We seek alternatives and quiet often it involves adding artificial flavours or sugars to our diets.
Get Colourful
Water is your body’s source of life. Being hydrated not only improves your health and naturally flushes toxins out of your body, but water also keeps your skin plump and elastic. Infused water is especially beneficial because it makes the act of drinking water more enjoyable, both for the taste buds and the eyes.
Avoid any fruit that’s bruised or overly ripe, or herbs that don’t look fresh. Add the fruit, herbs, spices or whatever you want to use into a bottle of cool water filtered or carbonated water. Use thin slices or small cubes because the flavor will infuse more quickly.
Fruit-infused water is best enjoyed after two-four hours or after it has had a chance to infuse overnight. The length of time it lasts depends entirely on the type of fruit and herbs you use. Basil, for example, only lasts for three days while heartier varieties like rosemary or thyme can last up to seven days.
Fruit infused water is naturally sweet and has only a few calories. As you see, there are plenty of reasons to drink fruit infused water. This beverage is not only healthy and delicious, it’s cost efficient and the kids can help too.
Get Fizzy
Carbonated water (also known as soda water, sparkling water, bubbly water, or fizzy water) is water into which carbon dioxide gas under pressure has been dissolved. … Most carbonated water is sold in ready to drink bottles as carbonated beverages such as soft drinks. Its refreshing and a good alternative to sugary drinks.
Did you know that you can make your own?
There are plenty of products water such as Soda Stream, Siphon Bottles and Home Co2 Keg Systems on the market today that enable you to quickly and cheaply create your own carbonated water.
Carbonated Water is Acidic
Carbon dioxide and water react chemically to produce carbonic acid, a weak acid that’s been shown to stimulate the same nerve receptors in your mouth as mustard. This triggers a burning, prickly sensation that can be both irritating and enjoyable for many people.
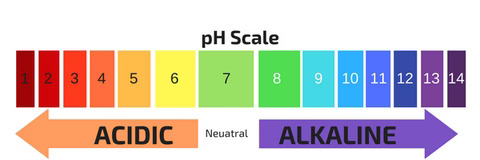
The pH of carbonated water is 3–4, which means it’s acidic. However, drinking an acidic beverage like carbonated water does not make your body more acidic. Your kidneys and lungs remove excess carbon dioxide. This keeps your blood at a alkaline pH of 7.35–7.45, regardless of what you eat or drink.
One of the biggest concerns about sparkling water is its effect on teeth, since the enamel is directly exposed to acid. Most studies done on this subject find that sparkling mineral water damaged enamel only slightly more than still water. Furthermore, it was 100 times less damaging than a sugary soft drink.
Is it bad for you?
There is currently no evidence that carbonated or sparkling water is bad for you.
It is not really that harmful for dental health and seems to have no effect on bone health.
Interestingly, a carbonated drink may even enhance digestion by improving swallowing ability and reducing constipation.
It’s also a calorie-free beverage that causes a pleasurable bubbly sensation. Many people prefer it over still water.
There’s no reason to give up this beverage if you enjoy it. In fact, it may actually improve your overall health.
Few things are as satisfying as an ice-cold glass of water on a hot day. But, it’s a lot more difficult to get the same satisfaction when the temperatures outside are freezing and the last thing on your mind is enjoying a cold beverage. Nevertheless, staying hydrated during the winter months is crucial if you want to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
There are plenty of reasons to increase your daily water intake, no matter what the season. But most importantly, your body needs water to function properly. Not only does water help you stay hydrated, it also helps regulate body temperature and is essential to the function of cells, tissues and organs.
As winter nears and temperatures begin to drop, the air becomes drier and our bodies receive less moisture than they do during warmer months. A major reason for this lower level of moisture in our bodies is that we tend to stop drinking as much water in winter months. During the summer months, it is easy to keep up with our water intake; our bodies’ thirst is a side effect of the heat and very few of us can go several hours without being thirsty
I Am Not Sweating
While we may not have the sunshine to keep us thirsty and craving water, the warmth from heaters, furnaces, and fires brings its own heat. Our bodies are mostly made of water – about 70% overall – and regardless of the time of year, requires good hydration. And while thirst is a good indicator of dehydration, it is a late indicator. During winter, symptoms include chapped lips, a dry cough, nosebleeds, mild headaches, and acne.
Keep the Winter Weight Away
When we are hydrated, our appetites are much more controlled. However, when we aren’t drinking enough fluids, we don’t have the energy required to break down fat; thus, we often mistake thirst for hunger, leading us to eat more than needed. Water is required for most of our bodily functions including regulating body temperatures, flushing toxins, and maintaining a healthy metabolism.
How Can You Ensure That You Stay Hydrated Through Winter?
As the temperature continues to drop, we find ourselves preferring a hot beverage to warm ourselves up. In the blistering winter, a glass of ice water seems less appealing. Luckily there are many other ways to get water into your system that don’t include a cold glass of water. Here are some suggestions:
- Try warming up with a nice cup of hot green tea, or even hot water with lemon. These two hot beverages will keep you cozy on a chilly winter’s day.
- Water-based foods – Fruits and veggies are a natural source of water and can also provide an invaluable source of vitamins and minerals. Watermelons, apples, grapes, and berries are just a few fruits that will keep your water intake up.
- Eat your soup – Clear soup is a great source of water. Brothy soups will warm your body and fill you up while providing you with the water you need to get through the day.
- Get a humidifier – Humidifiers release water into the air, helping to keep our bodies moisturized.
When you’re trying to get enough water, sometimes it’s just as important to know what not to drink. Both caffeine and alcohol can make your body even more dehydrated. Limiting your intake of soda, coffee and alcoholic beverages can help keep that needed hydration in your system where it belongs.
While drinking a glass of water during the summer months seems like a no brainer, it’s just as – if not more – important during the winter. By realizing just how important water is, supporting our bodily functions will keep you as healthy as possible, regardless of the season.
Think of your filter system in water filtration system as being like the motor in your car. If you don’t change the oil and oil filter regularly in your car, the oil will get dirty and stop lubricating the engine, the engine will wear out… and your car will grind to a holt.
Well, it’s much the same with a water filter cartridge.
The importance of clean safe drinking water can’t be understated. Water undoubtedly is the essence of life & the quality of the water that we drink can significantly determine the overall health of our body. Where you live and the quality of the water has a huge influence over how long your filter will last, for example, in an area with lots of contaminants in the water the cartridge just won’t last as long.
What can affect your filter?
- The overall condition of your water in terms of contaminants and how much must be filtered.
- If you have hard water (heavy with minerals) which causes the scale to build up and clog the filter.
- If you use more water than the average household.
- How well your water was previously treated or filtered.
Signs that your water Filter Needs Changing
- Your filtered water begins to taste different, In fact, if you can taste the chlorine in the water again you have gone past the use-by date of the filter.
- Your filtered water begins to smell different
- The water flow starts to slow down. This is because the filter is beginning to get clogged up with particles. When this happens, the filter still works but the carbon is not doing its job properly. Think of your filter like the dust filter bag in vacuum cleaner. Once the dust bag is full the vacuum cleaner will suck but at a reduced rate but it also often blows out stale air & dust as it tries to get clean in order to do its job. Like wise if a water filter cartridge is not changed, over time the carbon granules in the filter becomes less and less effective. Eventually it can’t capture the particles anymore to the point where it will become totally clogged up and not work at all…and could become a breeding ground for bacteria.
- When water is left in a glass for a few minutes, sediment is seen floating or settled at the bottom.
- Your water filter becomes discoloured
- You receive a call from our Customer Service team as a friendly reminder.
How often should I change my water filter?
The recommended filter change cycle varies from one product to the next. Home filtration systems usually have established “service cycles” based around average household usage, the quality of the water in the region where you live.
The service cycle may be for a specific number of litres of water or an estimate of the number of months that a cartridge will last in the average home. To ensure the filter continues to reduce contaminants, replace it according to the recommendations.
If you run into any of the signs that suggest that your filter requires changing Call us today on 1300 365 202